Asset dependencies
At this stage, you have several assets that are independent of each other. In most data platforms, assets are connected to form a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
To create a DAG, in this step, you will add another asset to your Definitions object and link it to the assets you previously defined.
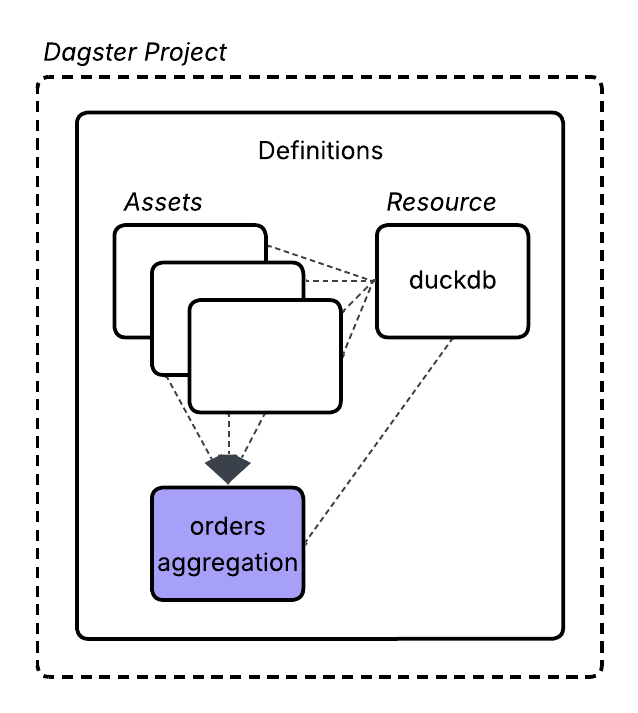
1. Create a downstream asset
Creating a downstream asset is the same as creating any other asset. In this step, you define a table that relies on the data from all of the assets you have already created.
To link the assets together, set the deps parameter within the asset decorator. Dagster uses this information to build the asset graph:
...
@dg.asset(
deps=["customers", "orders", "payments"],
)
def orders_aggregation(duckdb: DuckDBResource):
table_name = "orders_aggregation"
with duckdb.get_connection() as conn:
conn.execute(
f"""
create or replace table {table_name} as (
select
c.id as customer_id,
c.first_name,
c.last_name,
count(distinct o.id) as total_orders,
count(distinct p.id) as total_payments,
coalesce(sum(p.amount), 0) as total_amount_spent
from customers c
left join orders o
on c.id = o.user_id
left join payments p
on o.id = p.order_id
group by 1, 2, 3
);
"""
)
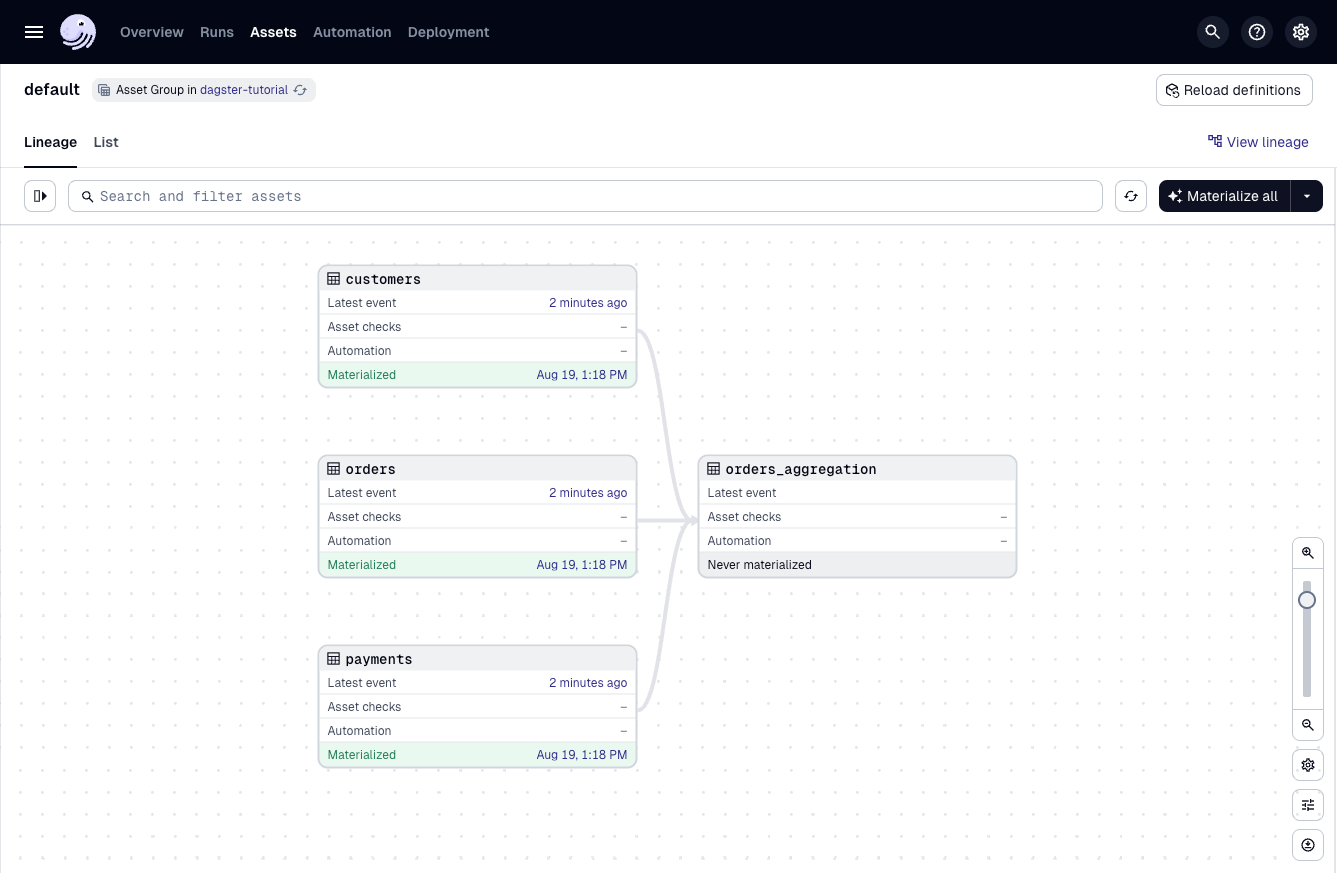
2. Materialize the assets
To view the updated asset graph:
-
In a browser, navigate to http://127.0.0.1:3000, or restart
dg devif it has been closed. -
Navigate to Assets.
-
Click Reload definitions.
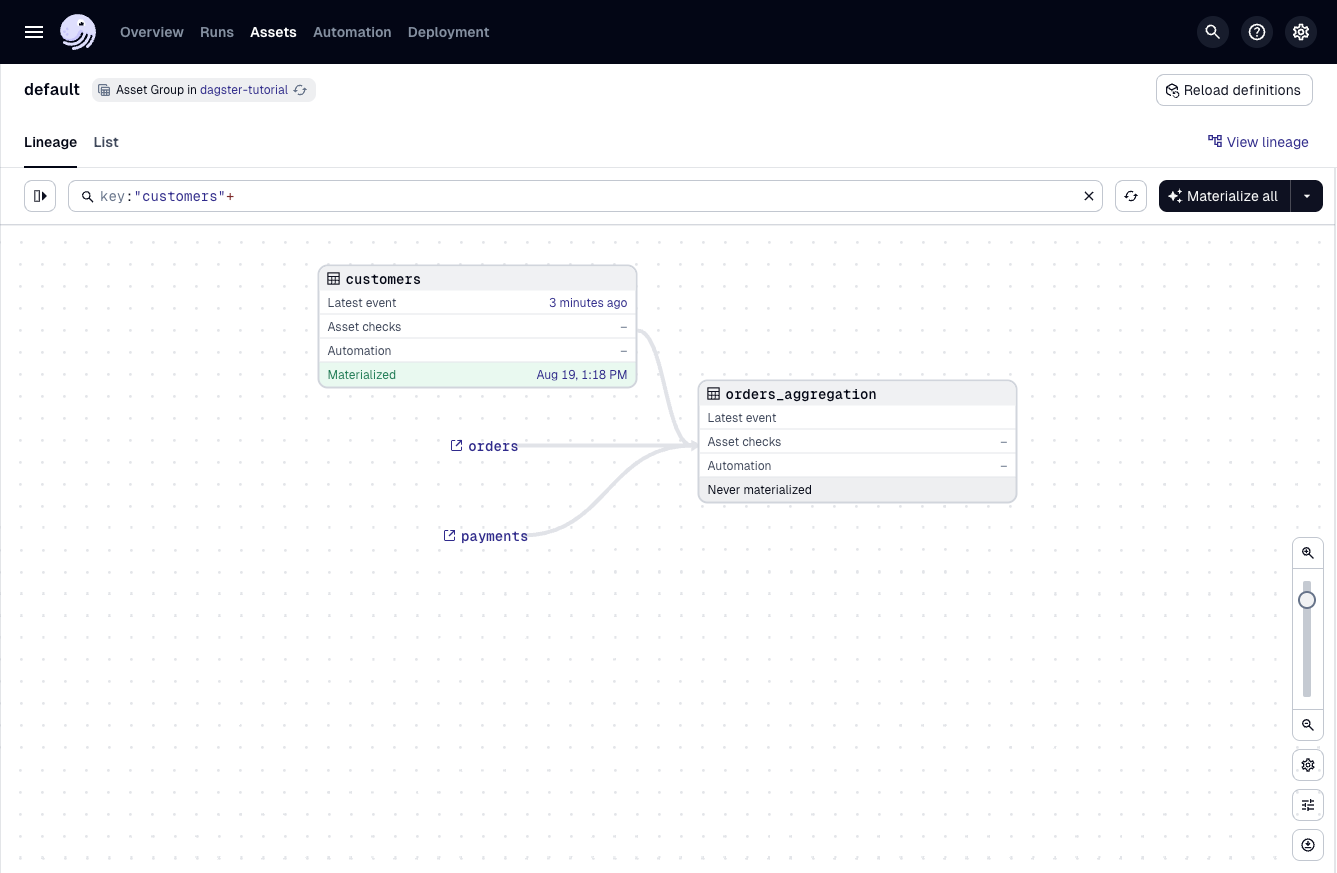
In Dagster, asset selection syntax provides a powerful and flexible way to specify exactly which assets to materialize, observe, or run in a job. You can select assets explicitly by their key (for example, customers) or use wildcard patterns and hierarchical paths to target groups of related assets.
To select all assets downstream of customers, use key:"customers"+. You can also chain selectors with logical operators to combine multiple sets.